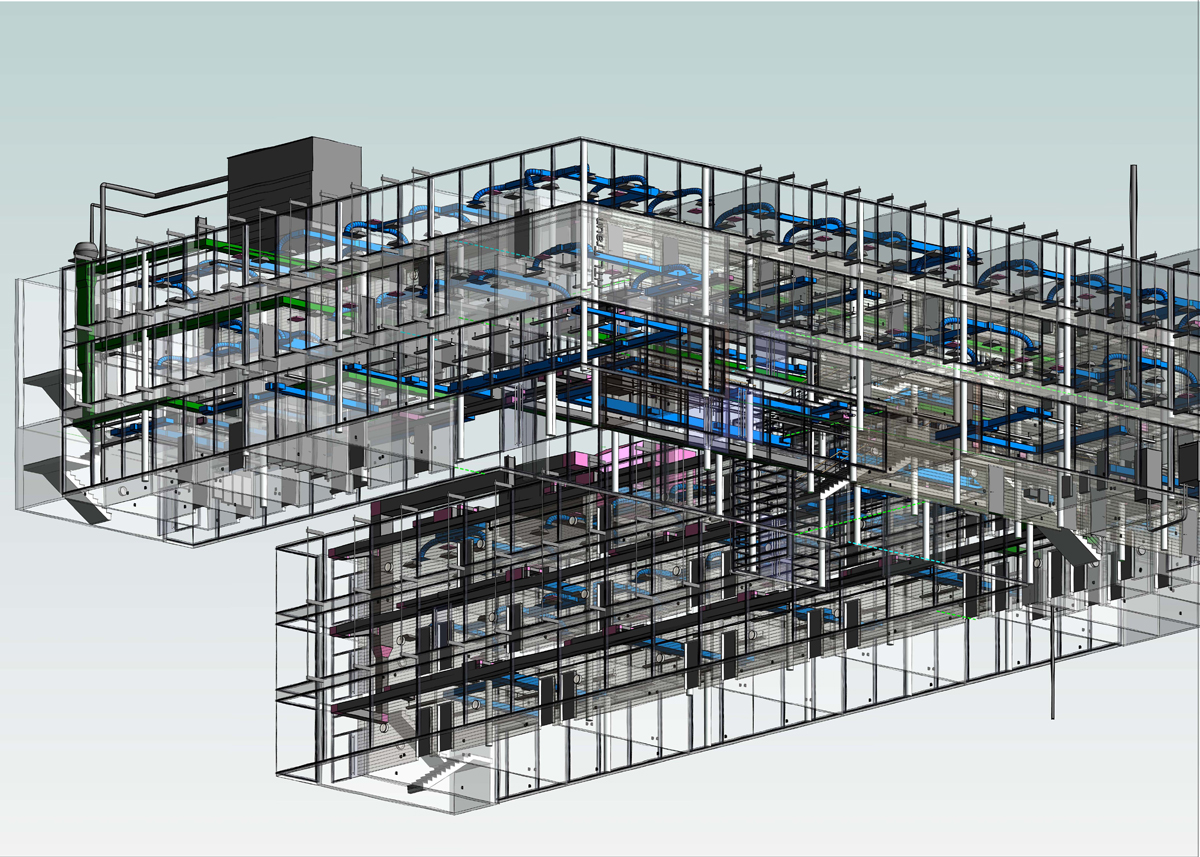
Clash Detection and Coordination in BIM
Building information modelling (BIM) has emerged not only as a transformative tool but also as a solution to practical challenges that occur on-site. In the modern construction industry, BIM is not just for design but also for solving practical challenges that occur on-site. One of its most important applications, clash detection and coordination, helps teams in identifying and resolving design before actual construction begins.
This important feature helps in saving significant time, money, and resources. Overall, the need for costly rework and on-site improvisation is reduced.
What is clash detection in BIM?
In traditional 2D drawings, clashes often remain hidden until the construction phase begins. Different elements of a building, in the form of structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, always have a chance of overlapping or colliding in the real world.
To avoid this, BIM’s 3D modelling capability brings these hidden conflicts to light during the design phase itself. In BIM workflow, clash detection is a digital process used to identify conflicts or “clashes” between different building elements within a 3D BIM model.
Types of Clashes
In BIM coordination, clashes are typically categorized into three main types
Hard Clashes
These occur when two physical components occupy the same space. For example, a structural beam running through an HVAC duct.
Hard clashes must be fixed in the design stage because they lead directly to expensive on-site rework if left undetected.
Soft Clashes (Clearance Clashes)
A soft clash happens when the required clearances or tolerances between elements are not maintained. For example, an air conditioning unit placed too close to a wall, making maintenance access impossible.
Soft clashes can cause operational and safety issues and often lead to code violations if not addressed.
Workflow or 4D Clashes
These happen when construction scheduling (4D BIM) reveals sequencing conflicts. It led to a delay in the execution of the project and resource conflicts.
For instance, installing ductwork before the supporting beam is in place.
How Does Clash Detection Work in BIM?
BIM software like Autodesk Navisworks, Revit, or Tekla Structures uses rule-based algorithms to automatically detect clashes. Here’s how the process typically works
Integration of Models
In large projects, different teams, such as architects, structural engineers, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) engineers, develop their own discipline-specific BIM models.
To detect clashes, these separate models are combined into a single, federated BIM model, which brings all building elements together in one coordinated digital space.
Running Clash Tests
Once the federated model is ready, the clash detection tool scans the entire project. It compares elements from different disciplines against each other based on predefined rules and tolerances—for example, checking whether pipes run into beams or if clearance spaces are maintained.
Generating Clash Reports
When a clash is found, the software generates a clash report that pinpoints the exact location and nature of the conflict. These clashes can be visualized directly in the 3D environment, making them easy to understand and discuss.
Coordination Meetings
To resolve clashes, project teams hold regular BIM coordination meetings, also known as clash resolution meetings. Here, stakeholders review the detected clashes together, decide who is responsible for fixing each issue, and agree on the best solutions collaboratively.
Model Updates
After the meeting, each team updates their discipline’s model to eliminate the clashes. The updated models are reintegrated into the federated BIM model, and new clash tests are run. This iterative cycle continues until the number of clashes is reduced to an acceptable level, ideally zero, before construction starts.
Benefits of Clash Detection and Coordination
Cost Savings
One of the biggest benefits is cost savings. Detecting clashes digitally during the design phase is far cheaper than fixing them on-site, where changes can lead to expensive rework, labor delays, material waste, and even contractual disputes.
Improved Collaboration
Clash detection encourages collaborative working between architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors. When different disciplines work in silos, miscommunication is common — but BIM coordination brings everyone together around a shared digital model.
Reduces On-Site Risks
Clash detection prevents last-minute improvisation and rushed fixes on-site, which often create unsafe working conditions. By resolving conflicts virtually, projects face fewer surprises and reduce the likelihood of unsafe site modifications, improving worker safety.
Better Quality and Safety
By eliminating physical and spatial conflicts before construction starts, BIM ensures that the design is accurate and buildable. This raises the overall quality of construction documents, making it easier for contractors to work efficiently and confidently on-site.
Challenges in Clash Detection
Incomplete or Poor-Quality Models
One major challenge is that clash detection is only as good as the input models. If the architectural, structural, or MEP models are incomplete, inaccurate, or not up to standard, the software won’t detect conflicts correctly.
Excessive or Irrelevant Clashes
In practice, automated clash tests often generate hundreds or even thousands of clashes — many of which may be trivial or unavoidable.
Lack of Standardized Clash Detection Rules
Different teams may set up clash tests using different tolerances or rules. Without clear project-wide standards, teams can interpret clashes differently, leading to misunderstandings or inconsistent clash reports.
Coordination Gaps Between Disciplines
Clash detection requires close collaboration among multiple disciplines. If teams work in silos, delays in sharing updated models can result in redundant clashes or conflicts that go unresolved for too long.
Software Limitations and Compatibility
Not all BIM tools integrate seamlessly with each other. If project teams use different software platforms or outdated versions, merging models can cause data loss, version conflicts, or import/export errors that affect clash accuracy.
Conclusion
In today’s complex construction projects, clash detection and coordination through BIM are no longer optional — they’re essential. By identifying design conflicts digitally and coordinating resolutions collaboratively, BIM saves time, money, and headaches down the line.
From skyscrapers to hospitals and bridges, BIM’s clash detection tools are ensuring that what’s designed on the screen can be built smoothly on the ground — with fewer surprises and greater confidence.
Contact Us
For a free quotation on your project requirements, feel free to contact us or email us at RAJ@SIMSONA.COM. Our experienced team is always ready and proud to support your project with precision and professionalism.

Send us
drawings and scope
Click the link below and send us your complete scope and drawings. We will provide quote/proposal in 24 to 48 hours.